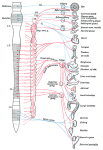
Central Nervous System
The limbic system is the area of the brain that maintains homeostasis and the hypothalamus is perhaps the most important part of the limbic system. It is the “brain” of the brain and is the single most intricate and amazing part of the brain. The hypothalamus controls homeostasis in the brain by way of feedback. The combined neurological and endocrine function of the hypothalamus allows is to play a prominent role is the regulation of numerous body functions.
The main function of the hypothalamus is homeostasis, or maintaining the body’s status quo. Factors such as blood pressure, body temperature, fluid and electrolyte balance, and body weight are held to a precise value called the set point. Although the set point can migrate from day to day it is remarkably fixed.
To achieve this task, the hypothalamus must receive inputs about the state of the body, and must be able to initiate compensatory changes if anything drifts out of range. The Hypothalamus constantly receives millions of nerve messages from complex areas of the rest of the Nervous system including the nucleus of the solitary tract, reticular formation, the retina, the circumventricular organs, the limbic and olfactory systems, sense organs, neocortex, osmoreceptors, as well as numerous touch receptors.
“The hypothalamus receives signals from all possible sources in the nervous system, thus, the hypothalamus is a collecting center for information concerning the internal well being of the body, and in turn, much of this information is used to control secretions of the globally important pituitary gland.” 11
This input into the hypothalamus allows it to regulate and integrate heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, digestion, emotional responses, behavior, sex drive, body and skin temperature, appetite, thirst and body fluids, sleep cycles, metabolism, and much more. The effectiveness of the hypothalamus is directly proportional to the functional capability of the nervous system to send and receive nerve messages and especially to maintain the integrity of those nerve messages as they travel along the spinal cord.
Spinal Cord & Nerve Interference
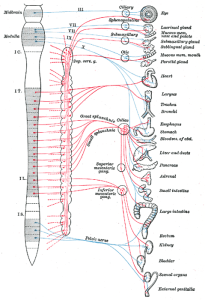
The spinal cord is both a cable and a switchboard. As a cable, it connects the brain with the rest of the nerves in body. As a switchboard, it coordinates muscle movements, reflexes and other activities under its direct control. The spinal cord is actually a direct extension of the brain, composed of the same kind of nerve cells, nerve fibers and supporting glial cells as those of the brain. It is also protected by the same three coverings (the meninges) and the same fluid (cerebral spinal) that house and protect the brain.
The spinal column is composed of 24 movable vertebrae. The spine is straight when looked at from the front or the rear. When viewed from the side, the spine forms a series of geometric curves or arcs. When the spine is in its optimum structural position, the nervous system is protected, and the integrity of nerve impulses traveling to and from the brain is at an optimum level. This is when the control system of the body can best achieve homeostasis.
Because the vertebra are moveable, they are also susceptible to certain stresses and forces which can cause them to lose their proper position. This leads to stress in the vital nerve system. This condition is known as a “vertebral subluxation”. Subluxations interfere with the normal flow of nerve impulses and can cause either an increase or decrease of nerve activity. Other references in the scientific literature which describe subluxations are: spinal lesions, nerve dysfunction, dysponesis, nerve impingement, neuritis.
Hormonal imbalances can be the result of either too much or too little glandular activity. Spinal Nerve interference and its resulting decrease in function may be a significant cause of endocrine dysfunction and hormonal related health problems.
“Lesions of the hypothalamic input region may produce a variety of symptoms, including diabetes, insipidous, obesity, sexual dystrophy, somnolence, and loss of temperature control” 12 Correlative Neuroanatomy & Functional Neurology
“Studies have shown that more than fifty percent of hyperthyroid patients have damage to the pathways in their nervous system” 13 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry
“Research at the A.T. Still Institute showed that spinal lesions resulted in pathological changes in the blood, urine, and tissue fluids. Spinal lesions of the atlas and axis ( C1& C2) were associated with abnormal function of the pituitary which resulted in abnormal hormone secretions. 14 Still Research Institute.
With few exceptions, hormone deficiency or hormone excess is the result of pathologic manifestations in the neural pathways that supply the hypothalamus. 15 Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
Causes of Vertebral Subluxations
Vertebral subluxations can be caused by any force or stress to which the body is unable to adapt. Examples of this would include automobile accidents, work related injuries repetitive motions events, sports and recreational pursuits, poor posture, poor bending, lifting and sleeping habits, and various types of chemical and emotional stress.
The body can adapt to the stress as long as the nervous and endocrine systems are capable of responding normally. All types of stress can not only cause vertebral subluxations, but it creates a viscous cycle in which the body can no longer adapt to stress as a result of a compromised nervous system.
Chiropractic
The purpose of Chiropractic is the detection and correction of vertebral subluxations which is accomplished by physically adjusting the spine. This restores the nervous system pathways to an optimum level of function, which maximizes homeostasis and the body’s inherent healing ability. Chiropractic is not a treatment for disease, nor do Doctors of Chiropractic claim to cure disease. Chiropractors simply remove nerve interference from the spine, and with a restored nervous system, the body is able to restore and maintain its own optimum level of balance.
Research studies as well as tens of thousands of case studies done in Chiropractic clinics have demonstrated that the correction of vertebral subluxations improves neurological function and health and allows the body to recover from a wide variety of health conditions, including many endocrine disorders.
Article originally posted at ICPA.org.